Setup mesos-dns
mesos-dns
To discover the services running on arbitrary mesos slave node, we need to use mesos-dns.
Here we will running mesos-dns service on mesos-slave-1, and set all slaves to use mesos-slave-1 as DNS nameserver.
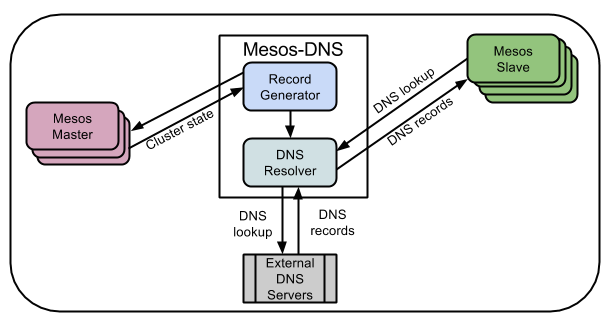
-
mesos-dns configuration file
In mesos-slave-1, edit /opt/mesos-dns/mesos-dns-config.json with the following content:
“resolvers”: upper-level dns nameserver.
“listener”: the ip address of mesos-slave-1
$ cat /opt/mesos-dns/mesos-dns-config.json
{
"zk": "zk://mesos-master-1:2181,mesos-master-2:2181,mesos-master-3:2181/mesos",
"refreshSeconds": 60,
"ttl": 60,
"domain": "mesos",
"port": 53,
"resolvers": ["10.240.0.1"],
"timeout": 5,
"httpon": true,
"dnson": true,
"httpport": 8123,
"externalon": true,
"listener": "10.240.0.5",
"SOAMname": "ns1.mesos",
"SOARname": "root.ns1.mesos",
"SOARefresh": 60,
"SOARetry": 600,
"SOAExpire": 86400,
"SOAMinttl": 60,
"IPSources": ["netinfo", "mesos", "host"]
}
-
Run mesos-dns as a marathon application
Make a marathon application config file for mesos-dns.
$ cat ./def-tasks/marathon-mesos-dns.json
{
"cmd": "sudo /opt/mesos-dns/mesos-dns -config=/opt/mesos-dns/mesos-dns-config.json",
"cpus": 0.2,
"mem": 256,
"id": "mesos-dns",
"instances": 1,
"constraints": [["hostname", "CLUSTER", "mesos-slave-1"]]
}
Run the mesos-dns application:
curl -i -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d@./def-tasks/marathon-mesos-dns.json mesos-master-1:8080/v2/apps
Configure each mesos-slave to use mesos-dns as nameserver
# ssh into each mesos-slave, and change the dns setting
sed -i '/nameserver/d' /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head
getent hosts mesos-slave-1 | awk '{ print "nameserver "$1 }' >> /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head
resolvconf -u
the above 3 commands are summerized in utils.sh so you can just call this command to change the dns nameservers of all slaves through gcloud compute ssh YOUR-SLAVE-INSTANCE:
./utils.sh -c set-slave-dns -n mesos-slave-1,mesos-slave-2,mesos-slave-3,mesos-slave-4
-
Test mesos-dns
We will run an marathon application: ‘hello-100-times’, and find it’s ip address through mesos-dns by its identity:
hello-100-times.marathon.mesos‘hello-100-times’ appication definition:
$ cat def-tasks/task-loop-hello.json
{
"id": "hello-100-times",
"cmd": "cnt=1; while [ $cnt -le 100 ]; do echo Hello $cnt times; sleep 3; cnt=`expr $cnt + 1`; done",
"mem": 32,
"cpus": 0.3,
"instances": 1,
"disk": 0.0,
"ports": [0]
}
Run 'hello-100-times':
curl -i -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d@./def-tasks/task-loop-hello.json mesos-master-1:8080/v2/apps
Mesos UI shows the app is running on slave-2
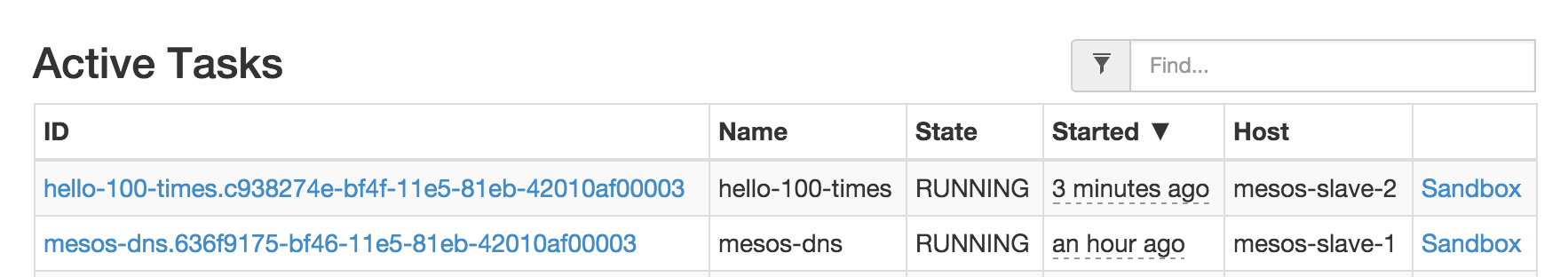
On every slave nodes, we can locate the app’s ip address by this identity: hello-100-times.marathon.mesos
$ ping hello-100-times.marathon.mesos
PING hello-100-times.marathon.mesos (10.240.0.6) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from mesos-slave-2.c.lab-larry.internal (10.240.0.6): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.648 ms
64 bytes from mesos-slave-2.c.lab-larry.internal (10.240.0.6): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.420 ms
...
$ ping mesos-slave-2
PING mesos-slave-2.c.lab-larry.internal (10.240.0.6) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from mesos-slave-2.c.lab-larry.internal (10.240.0.6): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.572 ms
64 bytes from mesos-slave-2.c.lab-larry.internal (10.240.0.6): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.372 ms